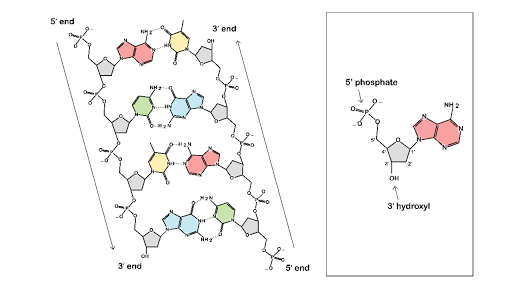
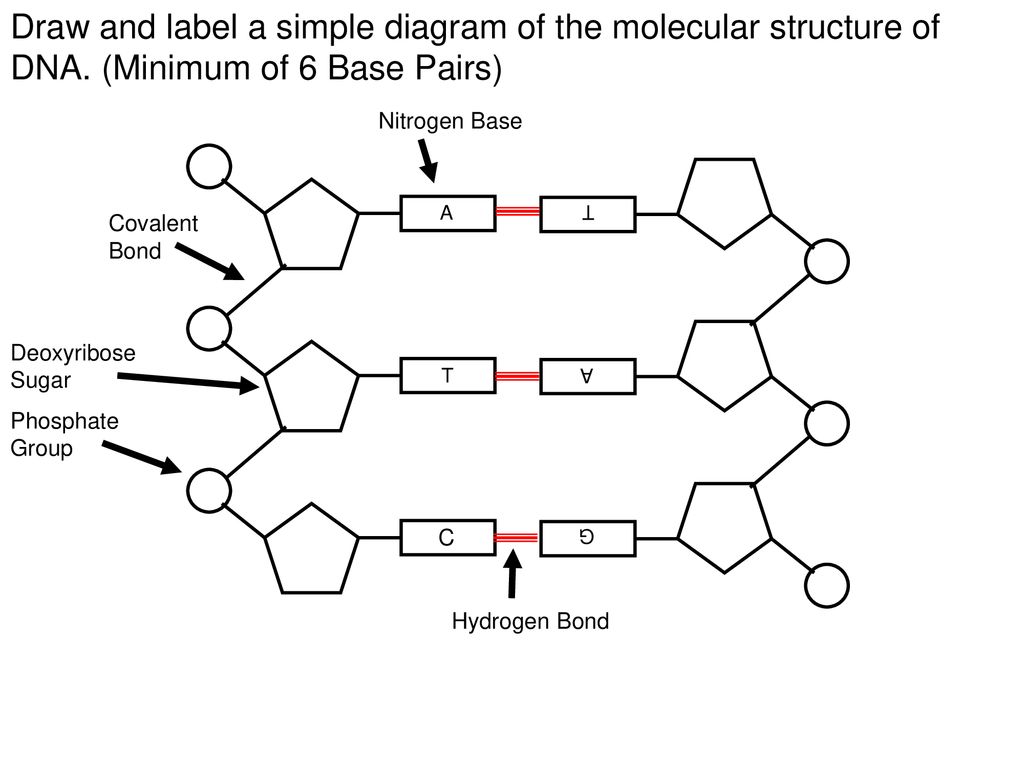
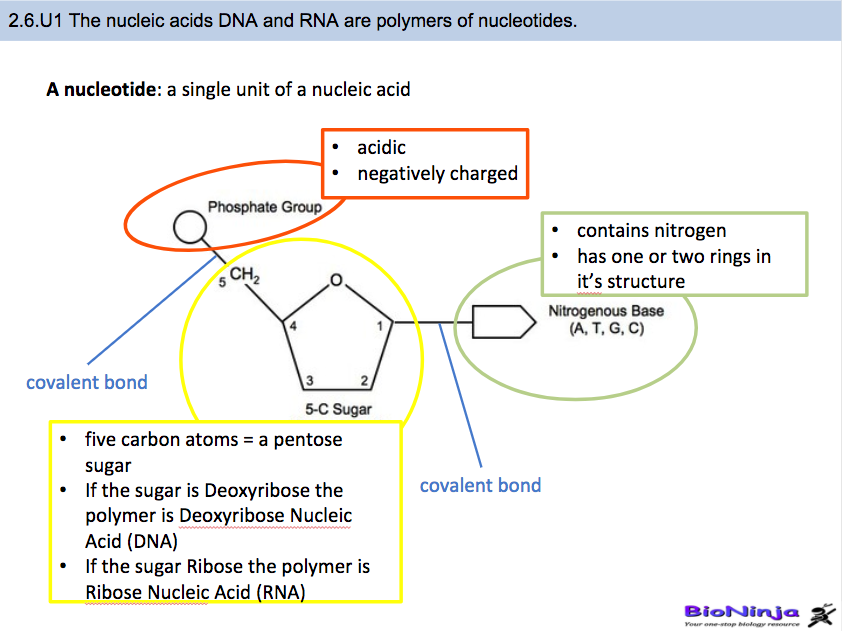
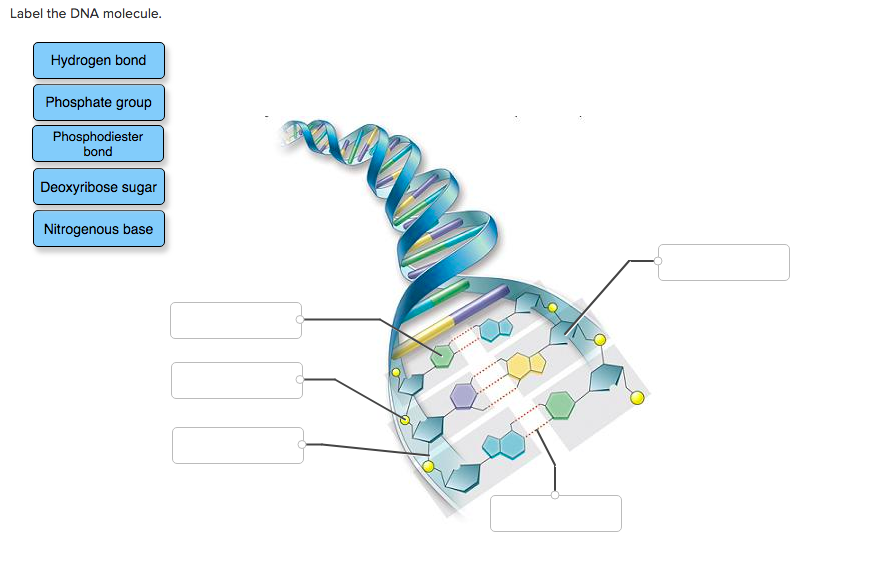
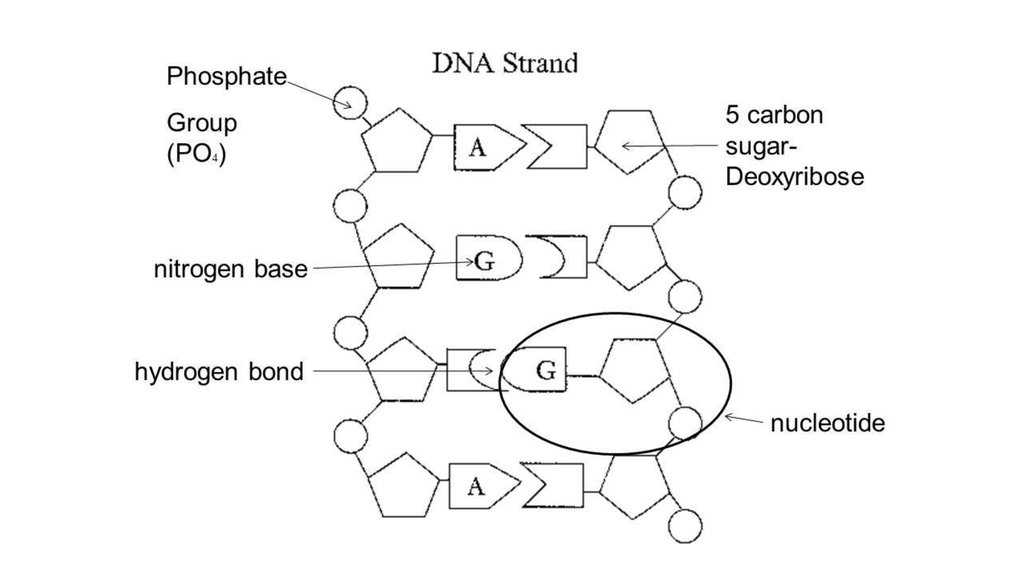
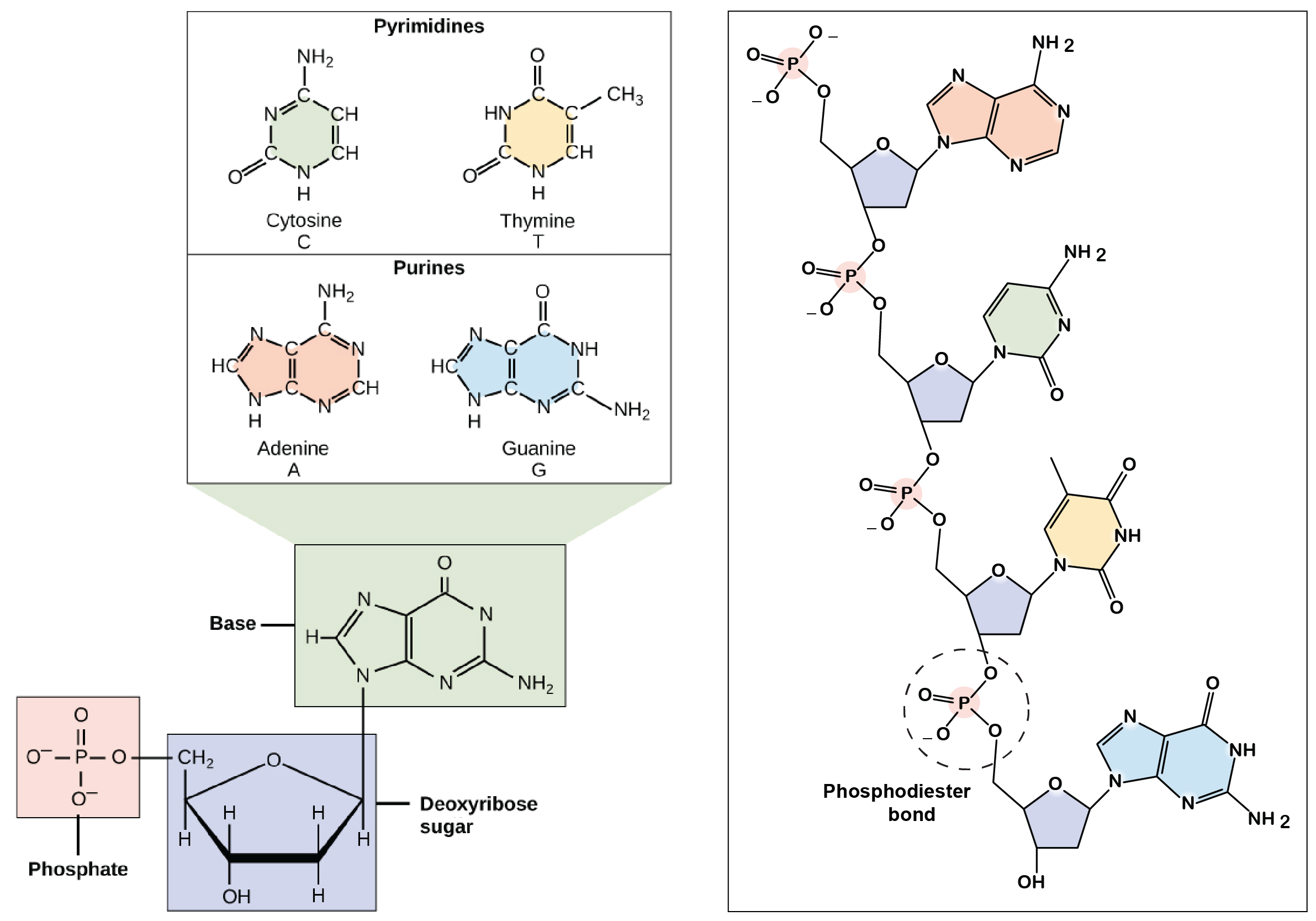
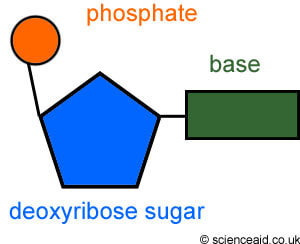
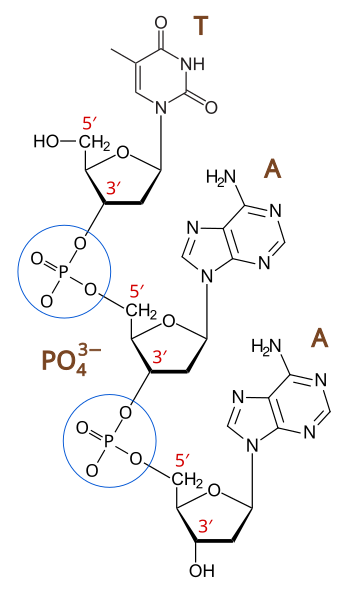
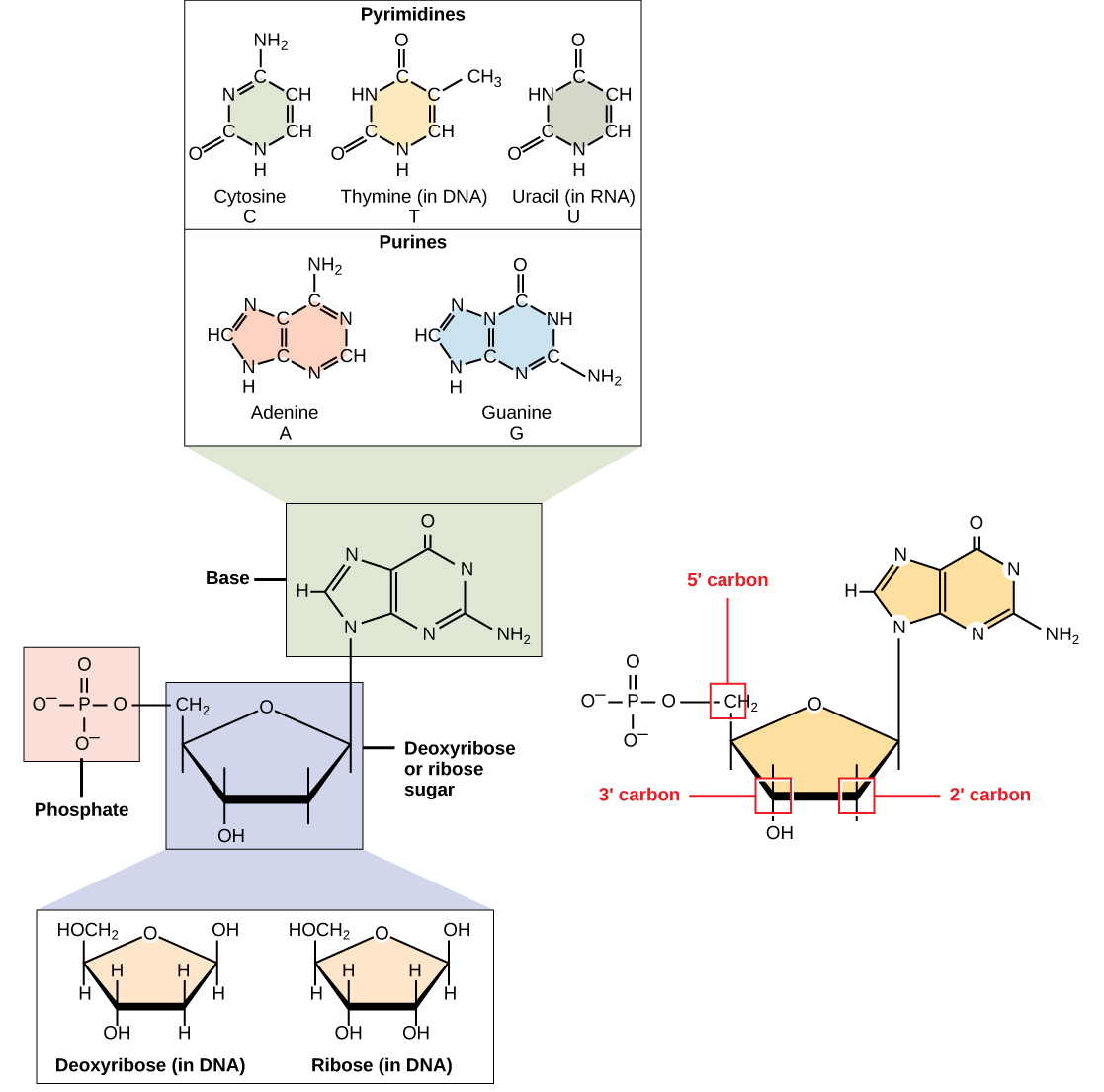
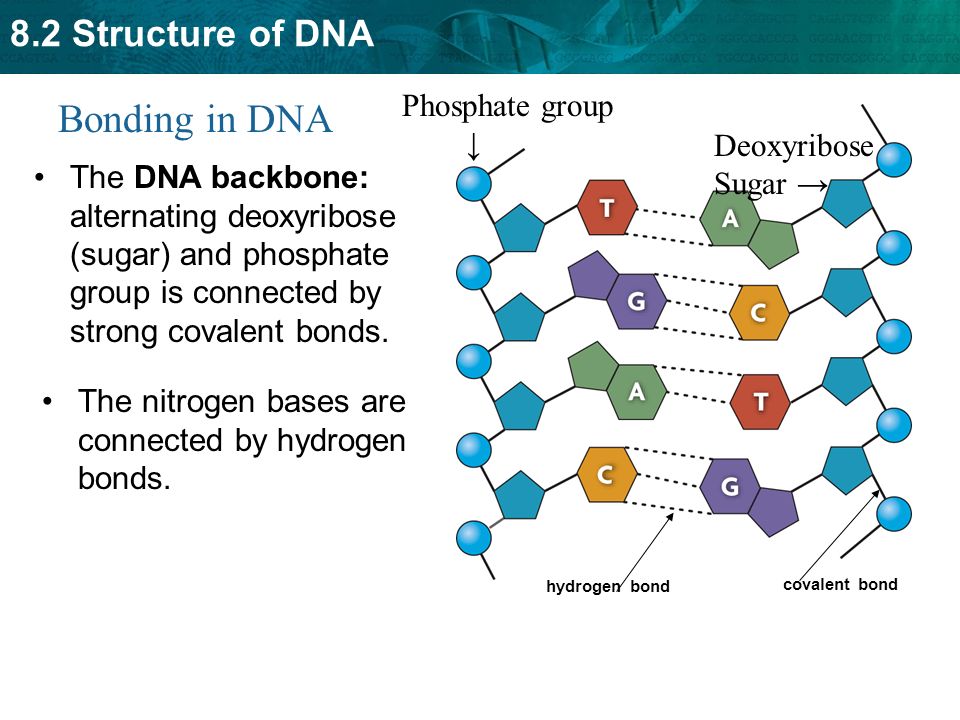
· In DNA a phosphate group (PO 43) is attached to the 3′carbon of deoxyribose sugar and 5′carbon of another sugarTherefore, each strand contains 3′ end and 5′ end arranged in an alternate manner Strong negative charges of nucleic acid are due to the presence of phosphate groupsOf one phosphate group, one sugar ring, and one nitrogencontaining base • DNA has 4 types of bases Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine (A, T, C, and G) These bases have strict binding rules, as A only bonds with T (and vice versa), and C only bonds with G This is important for DNA replication to workAnswer to Label the DNA molecule Hydrogen bond Phosphate group Phosphodiester bond Deoxyribose sugar Nitrogenous base

Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy
Model of dna and label the bases phosphate sugar groups hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds
Model of dna and label the bases phosphate sugar groups hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds-DNA Secondary structure is the set of interactions between bases, ie, which parts of strands are bound to each other In DNA double helix, the two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bondsThe nucleotides on one strand base pairs with the nucleotide on the other strand The secondary structure is responsible for the shape that the nucleic acid assumesHydrogen bond is a weak bond 4 The bond energy of covalent bond is between 100 to 1100 kJ/mol Bond energy of hydrogen bond is between 5 to 50 kJ/mol 5 Covalent bond is a primary bond Hydrogen bond is a secondary bond 6 Covalent bond changes the chemical properties of the bonding constituents



Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy
Nucleotide 3 What is the special shape of DNA called ?DNA Model DNA MODELS DUE This week you will construct a 3D model of DNA out of household junk Make sure that you include the sugarphosphate backbone and the nitrogen bases These beautiful works of art and science will hang in the room indefinitely, so be proud of what you do and take the time necessary to construct a nice modelAnd to explain the significance of such interactions to the primary and secondary structures of DNA
Answer choices the model is inaccurate because the base pairs are incorrect the model is accurate because it contains correctly paired bases the model is accurate because it shows each base splitting to form a double helix the model is inaccurate because some typical bases in DNA are missing s Question 85 The two strands of DNA are held together with hydrogen bonds between the nitrogen basesBase Pair = A base pair is two chemical bases bonded to one another forming a "rung of the DNA ladder" The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups Attached to each sugar is one of four basesadenine (A
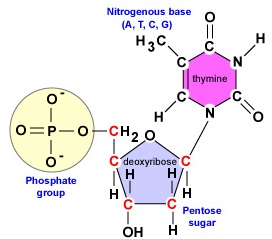
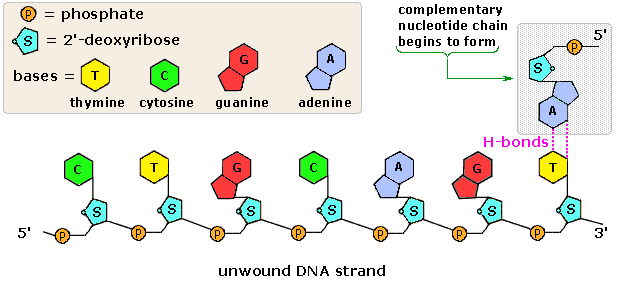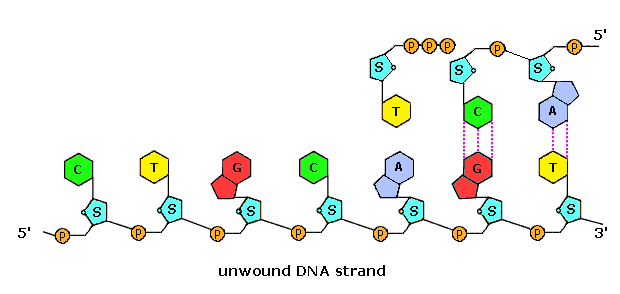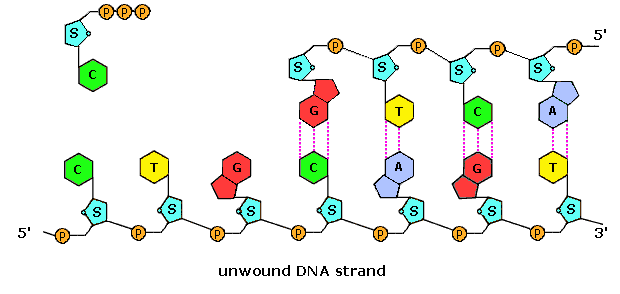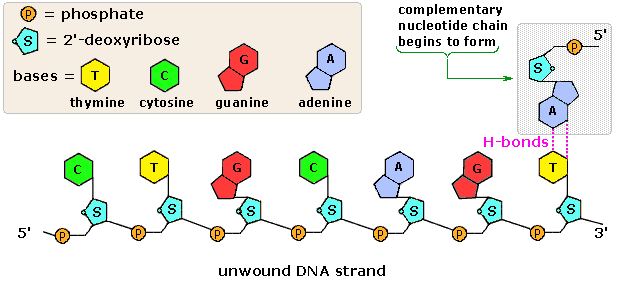
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) stores information for the synthesis of specific proteins DNA has deoxyribose as its sugar DNA consists of a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base The structure of DNA is a helical, doublestranded macromolecule with bases projecting into the interior of the molecule3 On the ladder model of DNA label each of the bases with the letter A, T, C or G 4 Refer to Model 1 When one nucleotide contains adenine, what type of base is the adenine attached to on the opposite nucleotide strand?Base Pairing in DNA The nitrogen bases form the doublestrand of DNA through weak hydrogen bonds The nitrogen bases, however, have specific shapes and hydrogen bond properties so that guanine and cytosine only bond with each other, while adenine and thymine also bond exclusively This pairing off of the nitrogen bases is called complementarity




Unit 3 Nucleic Acids And The Central Dogma Flashcards Quizlet



35 Dna Structure With Label Labels Design Ideas
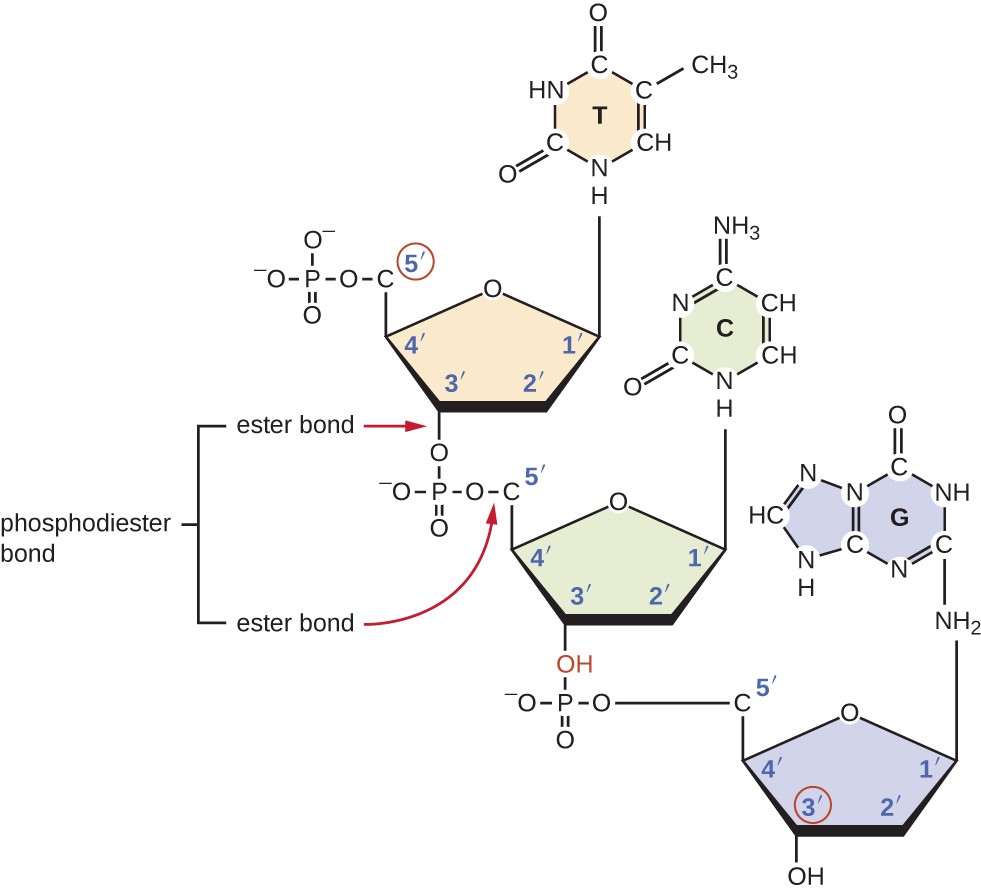
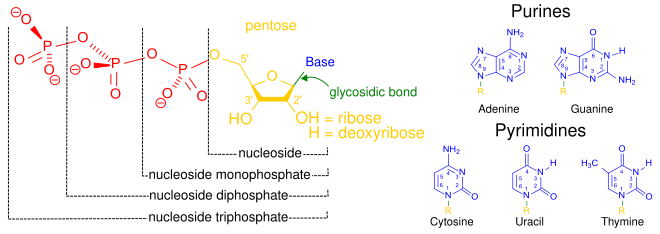
1 Label EVERY sugar (S), phosphate (P), and nitrogen base (A, T, C, G) in the diagram below 2 Examine the objects inside the box labeled #2 What is this called?When nucleotides are incorporated into DNA, adjacent nucleotides are linked by a phosphodiester bond a covalent bond is formed between the 5' phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3'OH group of another (see below) In this manner, each strand of DNA has a "backbone" of phosphatesugarphosphatesugarphosphate · The DNA double helix is stabilized primarily by two forces hydrogen bonds between nucleotides and basestacking interactions among aromatic nucleobases The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine , guanine (G) and thymine (T)These four bases are attached to the sugarphosphate to form the complete nucleotide, as shown for adenosine monophosphate




Bond Linking Monomers Types With Concepts Videos And Examples



Molecular Structure Of Dna Video Khan Academy
Label the entire DNA molecule (Be sure to include prime ends of a sugar molecule, pyrimidine and purine, nucleoside, nucleotide;1 Although weak, multiple hydrogen bonds are important in stabilizing the threedimensional shape of many biological molecules (Shape determines function "functional conformation") 2 Covalent bonds are usually very stable cells use protein catalysts called enzymes to "break" covalent bonds eg hydrolysi0519 · Watson and Crick model of DNA provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of doublehelix DNAA DNA is a polymer composed by the combination of several monomer units (deoxyribonucleotides) linked by the phosphodiester bondIn the discovery of DNA, many scientists have contextualized the structure of DNA, its components and composition etc



Dna Structure



2 6 Dna Rna Structure
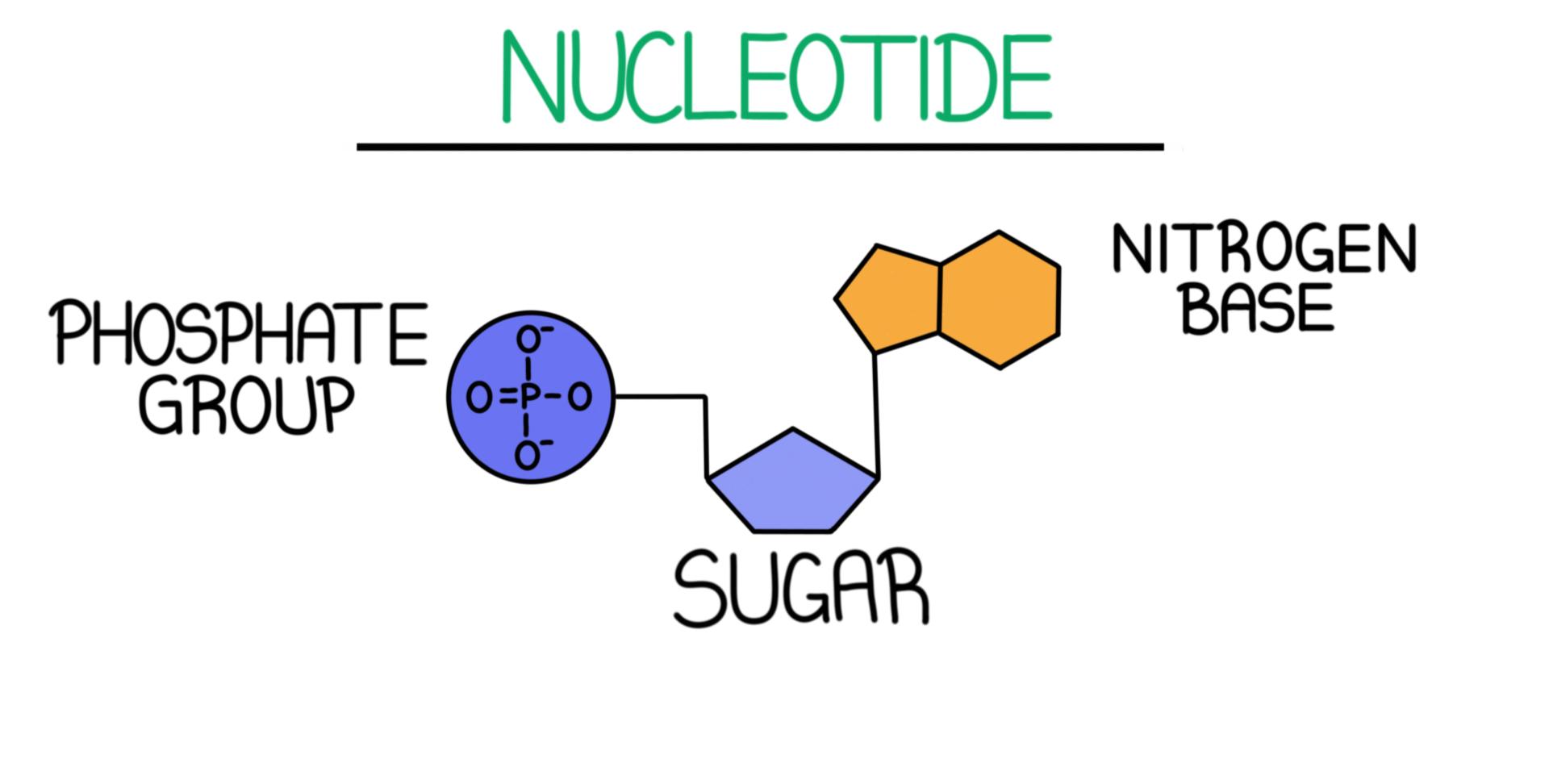
PRE uses blue light to break covalent bonds between thymine bases, allowing the hydrogen bonds to naturally reform Excision repair (dark reactivation) This repair process involves several enzymes a) An endonuclease called UvrABC 1 breaks the sugar phosphate backbone of the DNA strand near the dimer on each sideThe phosphate of one nucleotide is covalently bound (a bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms) to the sugar of the next nucleotide The hydrogen bonds between phosphates cause the DNA strand to twist The nitrogenous bases point inward on the ladder and form pairs with bases on the other side, like rungsThe nucleotides that comprise DNA contain a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group which covalently link with other nucleotides to form phosphodiester bonds Nucleotide bases can be classified as purines (containing a doublering structure) or pyrimidines (containing a singlering structure)



Sugar Phosphate Backbone The School Of Biomedical Sciences Wiki



9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
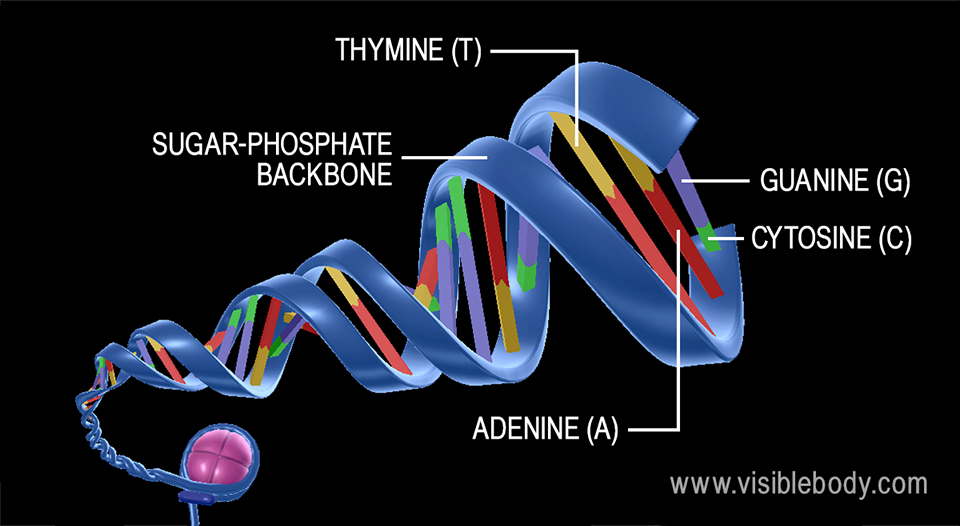
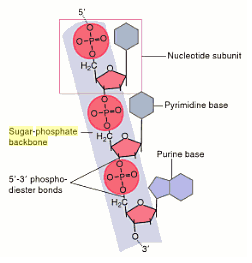
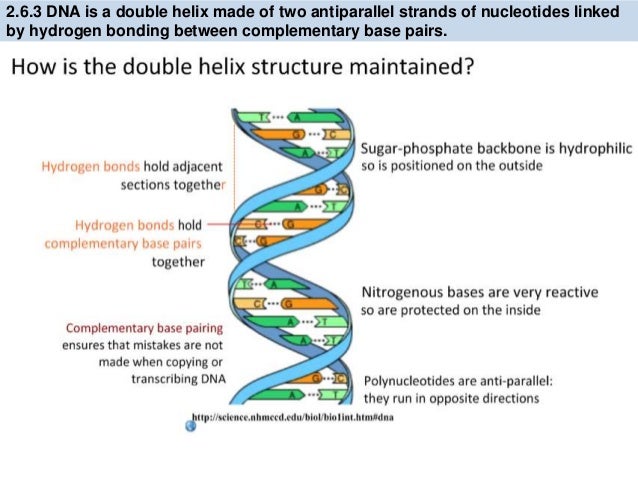
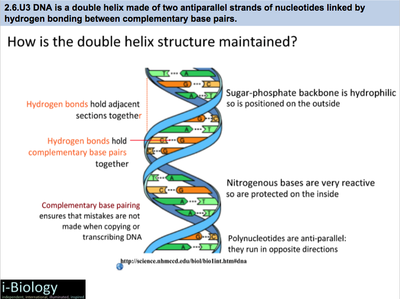
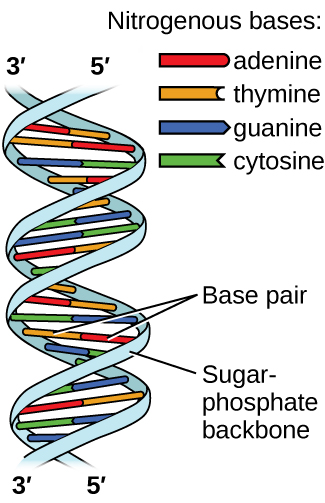
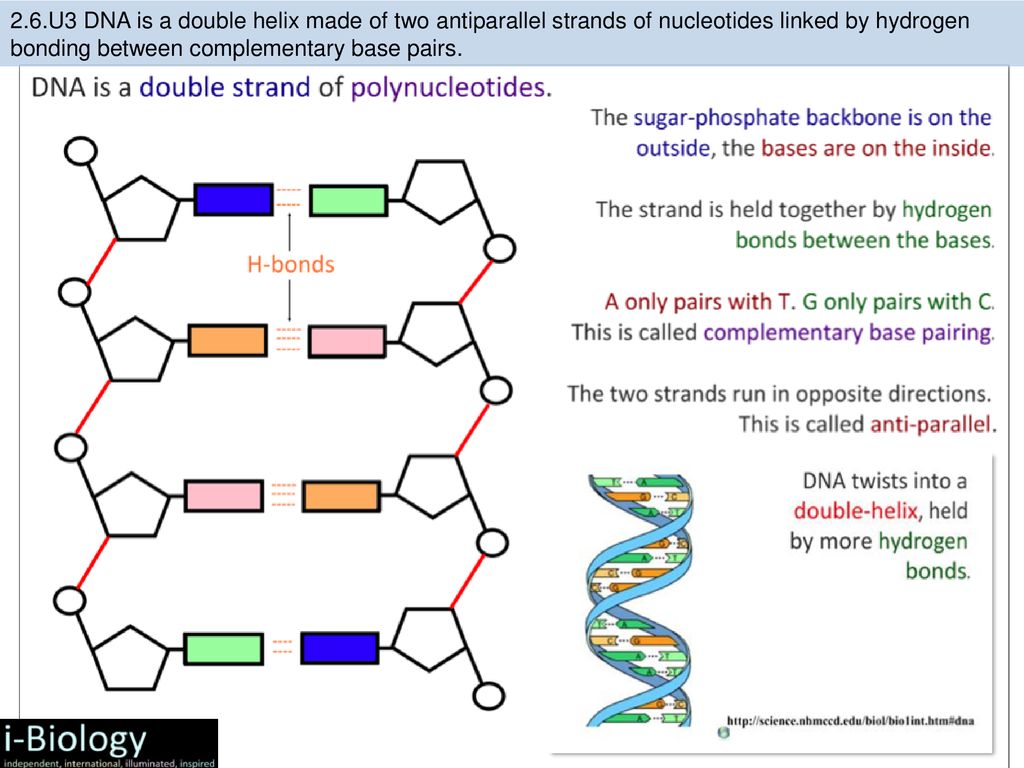
The rungs connecting the two sugarphosphate strands are created by pairs of nitrogenous bases These bases pair in very specific ways A always pairs with T and G with C Sugarphosphate Backbone Function The sugarphosphate backbone, as mentioned, is an important component of DNA's double helix structure · Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine and guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with cytosine The complementary base pairing in DNA is called WatsonCrick DNA base pairing model It brings two complementary DNA strands together, forming hydrogen bonds Hence, the final structure of DNA is doublestranded and antiparallelDNA has a doublehelix structure, with sugar and phosphate on the outside of the helix, forming the sugarphosphate backbone of the DNA The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior in pairs, like the steps of a staircase;



Solved 1 Which Of The Following Statements Describes Pu Chegg Com



Life Sciences Cyberbridge
A chemical bond between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of a neighboring nucleotide holds the backbone together Chemical bonds (hydrogen bonds) between the bases that are across from one another hold the two strands of the double helix together Bases There are four types of bases in DNA They are called * Adenine (A · Identified a hydrogen bonding arrangement between models of thymine and adenine bases, and between cytosine and guanine bases which fullfilled Chargaff's rule Figure 127 Chargaff's Rule Bonding Note that the "TA" pair can overlay the "GC" pair with the bonds to the sugar groups in similar juxtapositionThe backbone of DNA is based on a repeated pattern of a sugar group and a phosphate group The full name of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, gives you the name of the sugar present deoxyribose Deoxyribose is a modified form of another sugar called ribose




Dna Structure And Sequencing Boundless Biology




Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
Otherwise your DNA model will not fit together properly In DNA, a particular purine always bonds with a particular pyrimidine Adenine bonds to thymine and guanine bonds to cytosine The purines and pyrimidines are bonded together by hydrogen bonds Study Figure 6 to see how the nitrogen bases are bonded together in a DNA segmentCovalent bonds, hydrogen bonds, bases, deoxyribose, phosphate group, prime ends of each strand, backbone)Obtained Xray diffraction images of DNA determined that the DNA had the shape of a corkscrew or helix Watson and Crick discovered that the DNA molecule was a double helix of two strands facing each other built models of DNA



Life Sciences Cyberbridge




Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy
DNA Structure A, B and ZDNA Helix Families 4 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 02 Macmillan Publishers Ltd, Nature Publishing Group / wwwelsnet This is likely to be due in part to propeller twisting of the0516 · (i) Phosphoric acid, (ii) Pentose sugar, and (iii) Organic bases (i) Phosphoric Acid The phosphoric acid (H 3 P0 4) is biologically called phosphate and it was discovered by Levene in 1910Phosphoric acid (Fig 101) has three reactive hydroxyl groups (—OH) of which two are involved in forming sugar phosphate backbone of both DNA and RNADouble helix 4 Which type of chemical bonds will join the two DNA bases?



Ib Biology 2 6 7 1 Slides Dna Structure



19 3 Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Biology Libretexts
GROUP ACTIVITY This activity carries 10 marks You have to make a model of DNA 1 width of the model cms 2 Height 2 feet 3 Colour coding for phosphate, sugar and nitrogenous bases (A,T,G,C) 4 Helical structure with minor and major grooveDNA is made up of two nucleotide strands The nucleotides are connected together by covalent bonds within each strand The sugar of one nucleotide forms a covalent bond with the phosphate group of another The two strands themselves are connected by hydrogen bonds The hydrogen bonds are found between the bases of the two strands of nucleotidesAnswer choices Each strand of DNA contains a phosphate and sugar backbone The nucleotides of DNA may appear in a wide variety of sequences DNA is double stranded, and covalent bonds between identical nucleotides hold the strands together




2 6 And 2 7 Paper 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet



Chapter 8 From Dna To Proteins Ppt Video Online Download
· A phosphodiester bond is formed between two sugar molecules and a phosphate group This bond connects nucleotides, which form the backbone of a DNA or RNA chain DNA and RNA, as we know, are extremely important biomolecules found in living organismsThey are responsible for making us what we are—similar, and yet so uniqueThe polymer that you created is known as the sugarphosphate backbone of DNA It consists of alternating deoxyribose (sugar) molecules and phosphate groups In this backbone,a phosphate group joins two consecutive sugars together via a covalent phosphodiester bond Can you identify which carbon atoms on the deoxyriboseAnswer The DNA double helix is held together by two types of bonds, covalent and hydrogen Covalent bonds occur within each linear strand and strongly bond the bases, sugars, and phosphate groups (both within each component and between components) Hydrogen bonds occur between the two strands and involve a base from one strand with a base from the second in complementary pairing These hydrogen bonds




Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy



Solved Label The Dna Molecule Hydrogen Bond Phosphate Gr Chegg Com
The bond formed between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of an adjacent nucleotide is a covalent bond A covalent bond is the sharing of electrons between atoms A covalent bond is stronger than a hydrogen bond (hydrogen bonds hold pairs of nucleotides together on opposite strands in DNA) Thus, the covalent bond is crucial to the backbone of theThe Watson and Crick Model • The two sugarphosphate chains run in opposite directions This orientation permits the complementary bases to pair • The pairs of nitrogenous bases in a DNA double helix are held together by hydrogen bonds, as shown here • Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine · A DNA molecule is composed of two strands Each strand is composed of nucleotides bonded together covalently between the phosphate group of one and the deoxyribose sugar of the next From this backbone extend the bases The bases of one strand bond to the bases of the second strand with hydrogen bonds




28 3a The Structure And Sequence Of Dna Medicine Libretexts




Primary Dna Molecular Structure
· A nucleotide is a structure made up of pentose sugar, a nitrogencontaining base (nitrogenous base) and phosphate The nucleotide is a structural building block of DNA Each nucleotide joint with the nucleotide of another strand with the hydrogen bond and other adjacent nucleotides with the phosphodiester bondThis is a ballandstick model of a DNA base (image from http//csboisestateedu/~amit/teaching/342/lab/structurehtml) Note how I call it "a ballandstick model1 Thymine and 1 adenine molecules the arrowheads represent the 3' ends of the strands this is a double stranded DNA the nitrogenous bases are paired correctly Hydrogen bonds are not shown but are suggested by the base pairing in the model The arrowhead represent the phosphate group at the end of the strand



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




Solved The Parts Of The Drawing Below Include All Of The Chegg Com
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is in the family of molecules referred to as nucleic acids One strand of DNA has a backbone consisting of a polymer of the simple sugar deoxyribose bonded to something called a phosphate unit Very unimpressively then, the backbone of a strand of DNA resembles this sugarphosphatesugarphosphatesugarphosphatAnother conformational range, frequently observed when studying DNA duplexes containing damaged bases, is syn, in which the bulky part of the bases points towards the sugar Purine and pyrimidine bases can interact through formation of hydrogen bonds, defining what is known as Watson–Crick basepair alignments, a common, but not unique, motif of secondary structure in DNADNA consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups Attached to each sugar is one of four basesadenine (A), cytosine , guanine (G), or thymine (T)




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna



Anatomy And Physiology Levels Of Organization The Chemical Level Of Organization Viva Open
The pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds The two strands of the helix run in opposite directions, so that272 DNA Base Pairs After completing this section, you should be able, given the necessary Kekulé structures, to show how hydrogen bonding can occur between thymine and adenine, and between guanine and cytosine;




3 3 Dna Structure Sl1 Biology Ferguson



3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja




Label The Parts Of The Drawing Below Include All Of These Terms Nucleotide Phosphate Sugar Brainly Com




Biology Chapter 16 17 Flashcards Quizlet
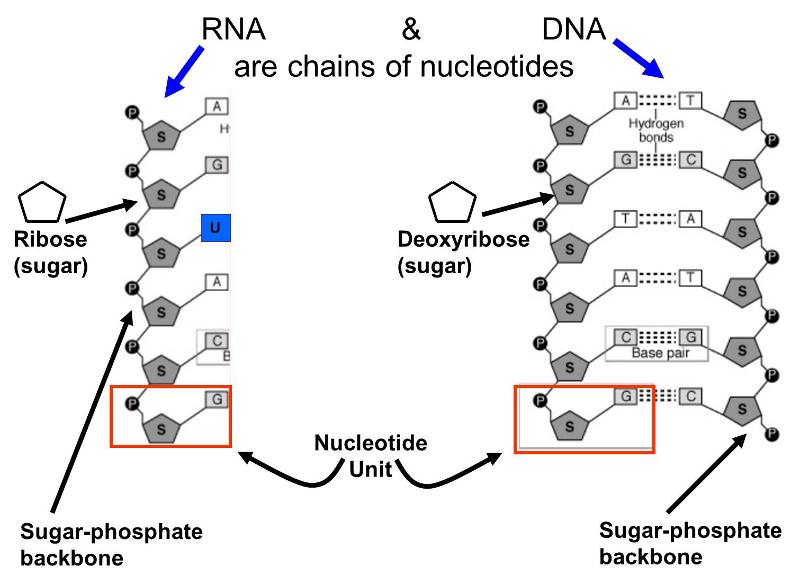



Nucleic Acids
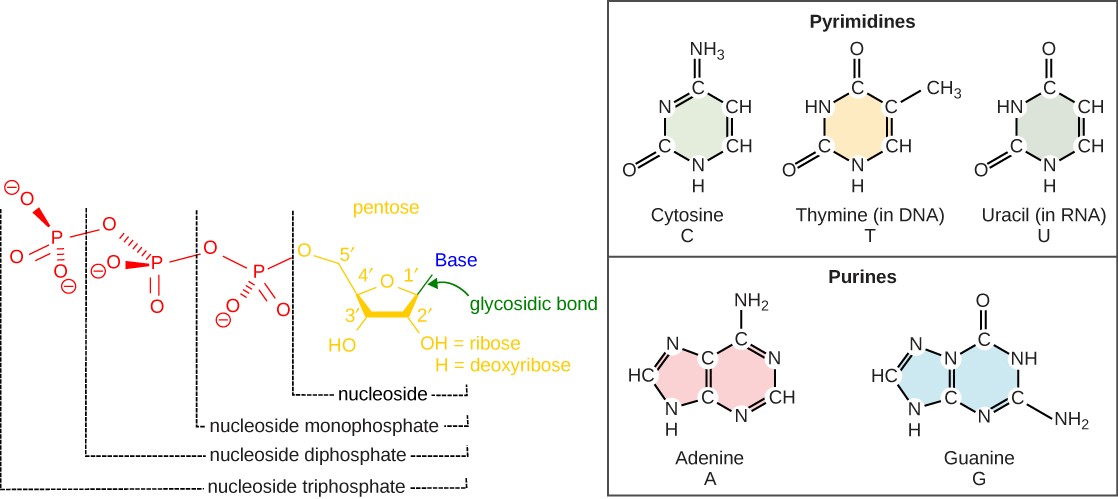



Chapter 5 Nucleotides Nucleic Acids Introduction To Molecular And Cell Biology




3 3 5 Draw A Simple Diagram Of Dna Structure Youtube




Click Here Test Bank Doctor
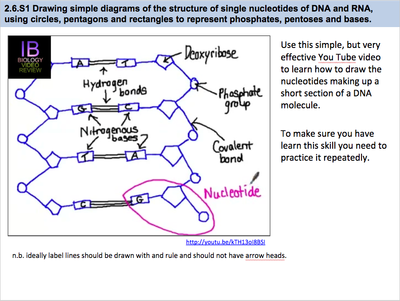



2 6 Dna Rna Structure




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna
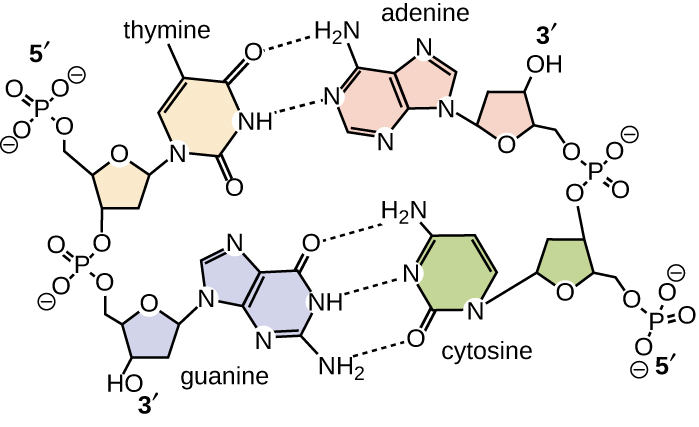



11 2 Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology Canadian Edition
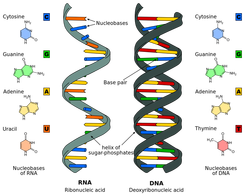



Topic 2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Nucleotide Definition Structure 3 Parts Examples Function



3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja
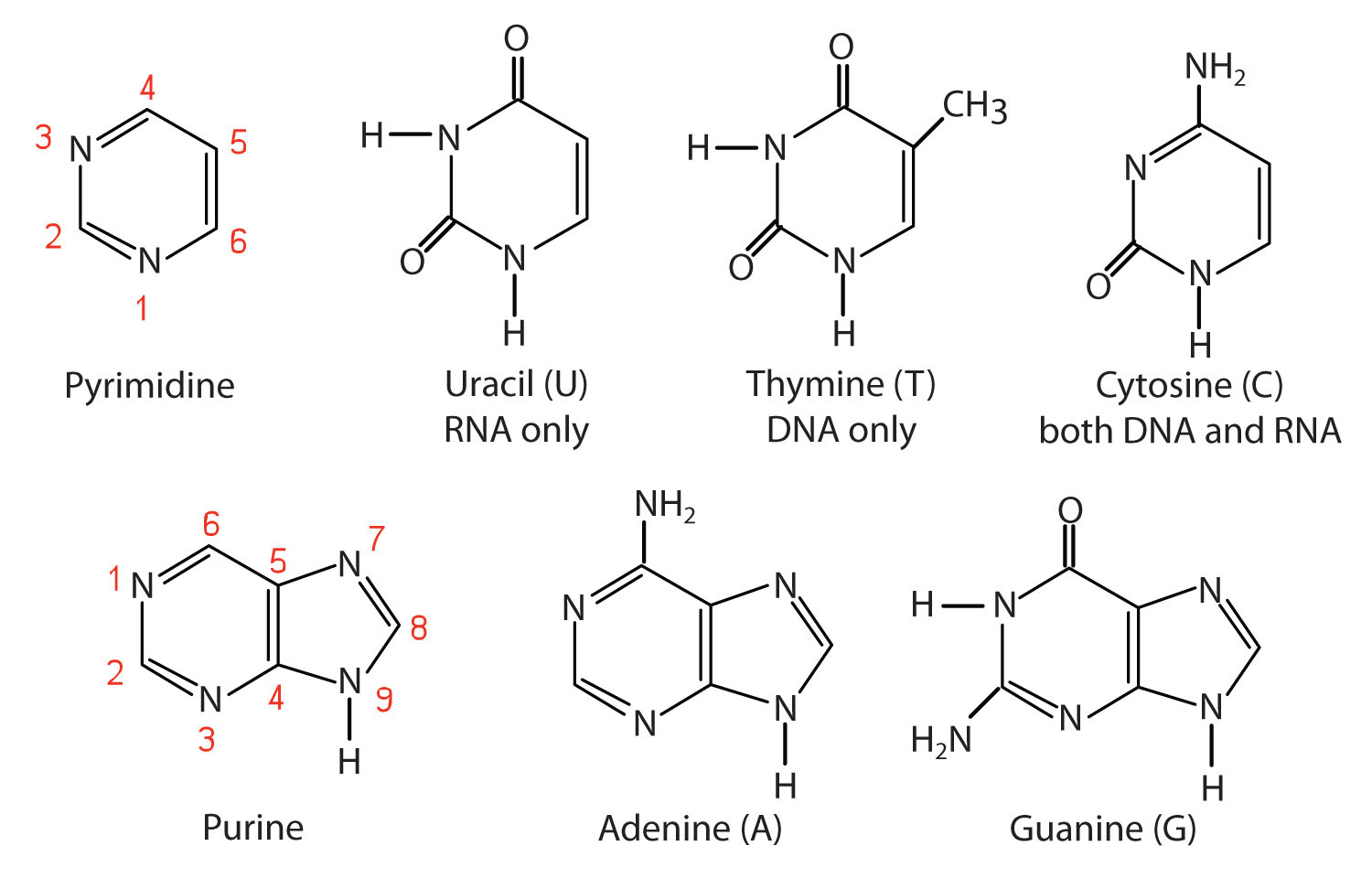



Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs
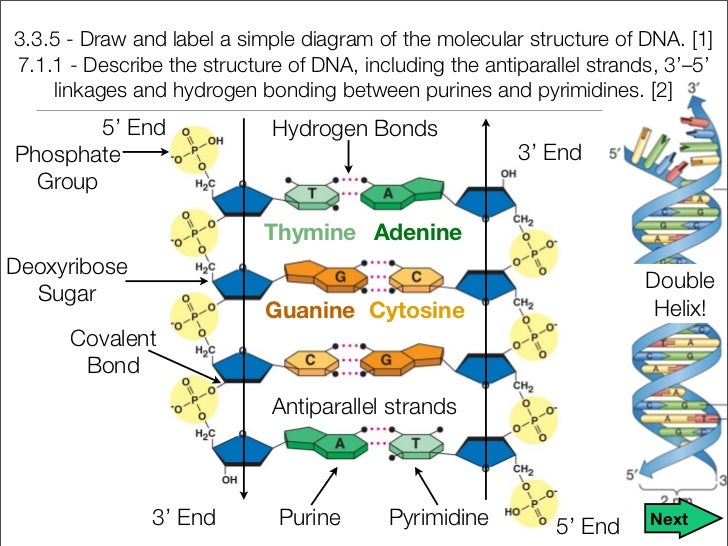



Unit 9 Dna Rna And Proteins Notes




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna




Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy




What Are The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide




Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy



h5425 Molecular Biology And Biotechnology
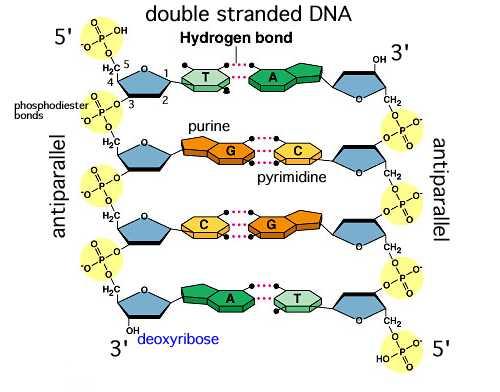



Exam 2 Dna Structure Replication Flashcards Chegg Com
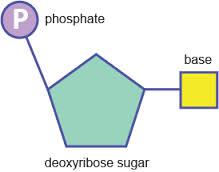



Topic 2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna




2 6 And 2 7 Paper 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet




Solved Gar Molecule Found In Dna Contains Iou A What Is Chegg Com



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology



What Are Chemical Bonds In Dna Quora



Life Sciences Cyberbridge
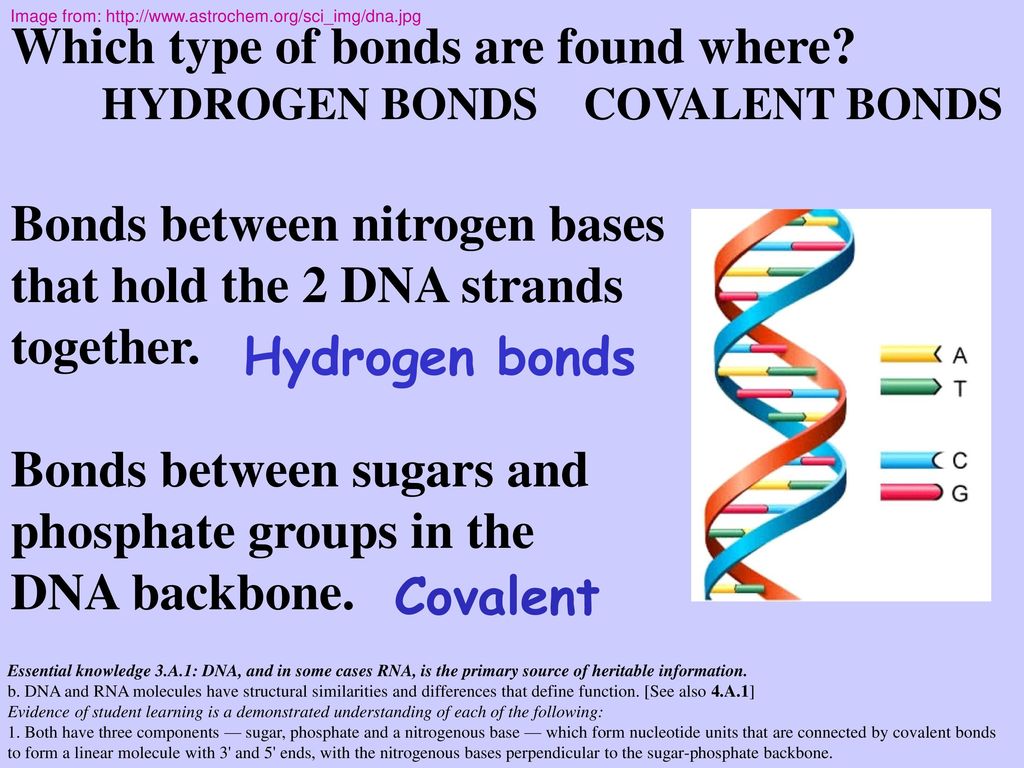



Review Chemistry Water Carbon And Molecules Chapters 2 3 Biology In Focus Chapters Campbell Kelly Riedell Brookings Biology Remember Biology Ppt Download




Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology




30 Dna Model With Label Labels Database
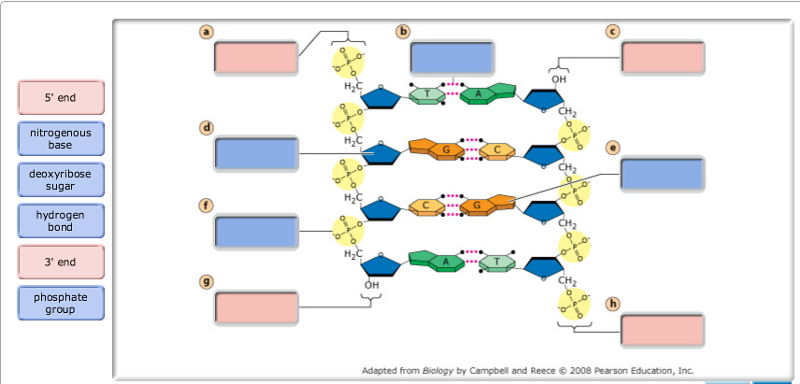



Exam 3 Chs 5 Dna Structure And Replication Machinery 16 The Molecular Basis Of Inheritance Flashcards Easy Notecards



3 3 1 3 4 3 Dna Structure And Replication Flashcards Quizlet



Life Sciences Cyberbridge



Life Sciences Cyberbridge




Mastering Biology Chp 13 Hw Flashcards Quizlet



Ch103 Chapter 5 Covalent Bonds And Introduction To Organic Molecules Chemistry



The Structure Of Dna




Lesson Explainer Dna Discovery And Structure Nagwa




Deoxyribose An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Functions And Structures Of Dna And Nucleotide Prezentaciya Onlajn




Unit 3 Nucleic Acids And The Central Dogma Flashcards Quizlet




Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs



Intermolecular Forces Chemistry 2e




Dna Structure Hs Tutorial Sciencemusicvideos



Dna Structure And Sequencing Boundless Biology




The Dna Double Helix Ck 12 Foundation



Dna Structure Overview Diagrams Expii



Life Sciences Cyberbridge



Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy




Structural Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Dna Dna Structure Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Topic 2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green



3 3 5 Draw A Simple Diagram Of Dna Structure Youtube




Sugar Phosphate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Principles Of Biochemistry Nucleic Acid I Dna And Its Nucleotides Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



1 1 The Structure Of Dna Biology Libretexts




Label The Diagram Use These Choices Nucleotide Deoxyribose Phosphate Group Nitrogenous Base Brainly Com




Dna Is A Double Stranded Molecule How Are The Adjacent Nucleotides In A Single Strand Of Dna Joined Together A Hydrogen Bonds Between Adenine And Thymine And Cytosine And Guanine B Hydrogen Bonds



3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja



Nucleic Acids




Dna Structure And Replication Flashcards Quizlet




Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy




Chemistry Ii Water And Organic Molecules



Nucleotide Wikipedia



Key Concept Dna Structure Is The Same In All Organisms Ppt Video Online Download




Dna Structure Overview Diagrams Expii



2 6 Structure Of Dna And Rna Ppt Download
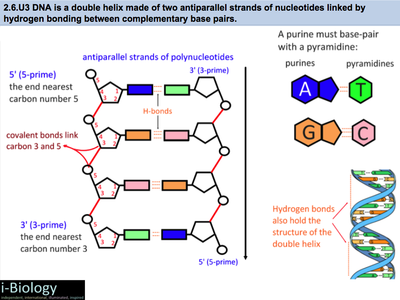



2 6 Dna Rna Structure



Chapter 10 Nucleic Acids And Protein Synthesis Che 1 Introduction To Organic Chemistry Textbook Libguides At Hostos Community College Library




07 1 Dna Structure Bisbiology12




Reading Review Sq3r Virginia Tyberg S Biology 1 Portfolios




Dna Structure Hs Tutorial Sciencemusicvideos



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿